Carbon Dioxide Cycle

Cycle on Earth is the carbon cycle.
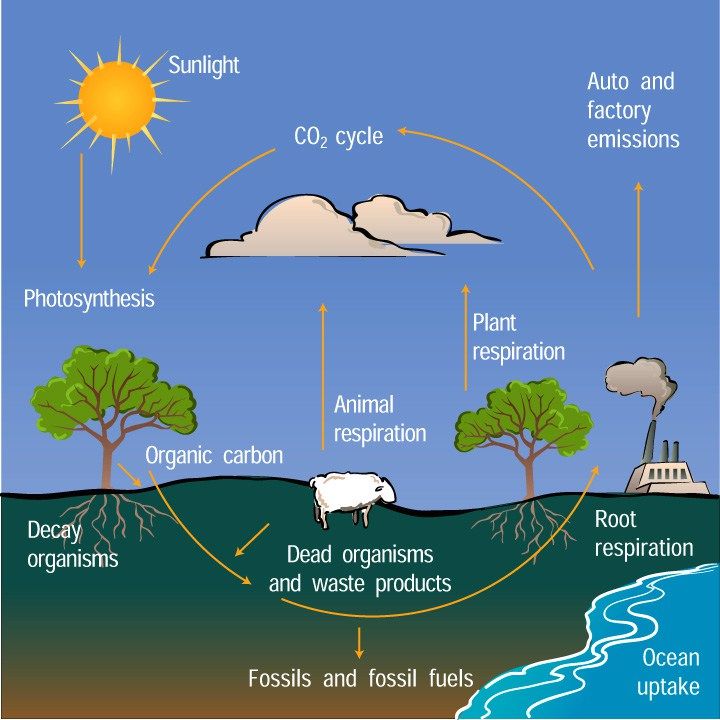
Carbon dioxide cycle. Carbon enters the atmosphere as CO2 CO2 is absorbed by autotrophs such as green plants. They act separately but are dependent on each other because the carbon cycle gives off oxygen for the oxygen cycle to use and in turn the oxygen cycle emits carbon dioxide CO 2 which goes back into the carbon cycle. Because the Earth is a dynamic place carbon does not stay still.
2012 Farlex Inc. Carbon dioxide is released by organisms as they break down by glucose. The effects of the slow carbon cycle such as volcanic and tectonic activity are not included.
The Oxygen-Carbon Dioxide Cycle. However carbon dioxide is also released by decaying organic matter geological processes and the burning of fossil fuels. It is currently emitted as a waste product in the form of CO 2 and is one of our principle climate change agents.
Carbon moves from plants to animals. The oxygen cycle and the carbon dioxide cycle carbon cycle are two of the biogeochemical cycles on Earth that make life possible. Autotrophic organisms like plants use carbon dioxide and sunlight to create glucose.
The carbon cycle is natures way of reusing carbon atoms which travel from the atmosphere into organisms in the Earth and then back into the atmosphere over and over again. Carbon is a vital component of every life form on our planet. This is the long-term carbon cycle.
The entry of carbon in the form of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere marks the start of the carbon cycle. These carbohydrates are ultimately oxidized by heterotrophic organisms to extract useful energy locked in their chemical bonds. In the Northern Hemisphere winter when few land plants are growing and many are decaying atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations climb.