Decomposition Carbon Cycle

The carbon cycle really is about life and death says Melanie Mayes a geologist and soils scientist at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee.
Decomposition carbon cycle. Hide Show resource information. Carbon is a major component in carbohydrates fats and proteins. What conditions would be best for the decomposition process.
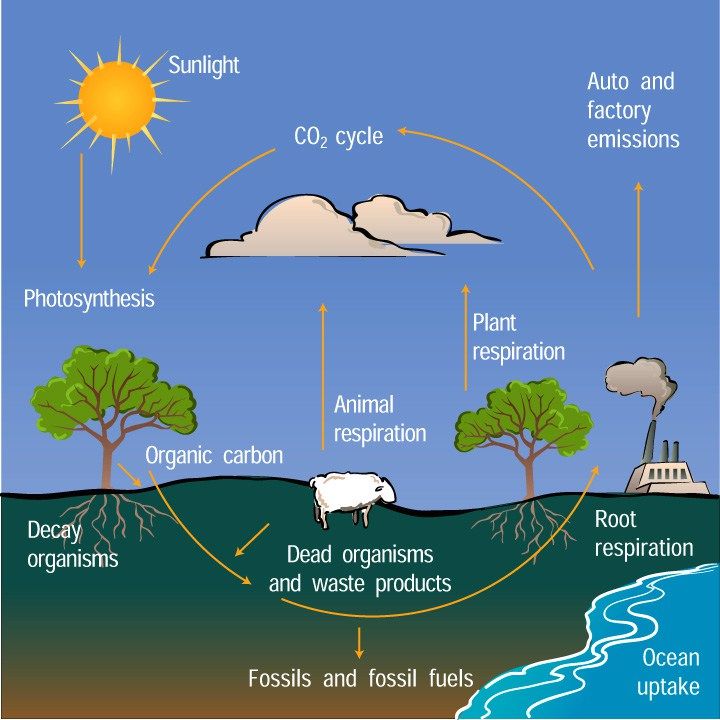
Before Earth had life on it carbon dioxide gas likely came from volcanic activity and asteroid impacts. Decomposition releases the chemicals that are critical for life Decomposers mine them from the dead so that these recycled materials can feed the living. Carbon present in the atmosphere is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis.
Soil organisms the physical environment and the quality of the organic matter Brussaard 1994. Carbon dioxide gas CO 2 can be produced by inorganic processes or by the metabolisms of living things. The carbon cycle is the cyclical movement of carbon atoms from the atmosphere to the biospherelithosphere and back to the atmosphere Figure 1.
These animals and plants eventually die and upon decomposing carbon is released back into the atmosphere. Microbes and other decomposers respirate and. Carbon Cycle Steps Carbon in the Atmosphere.
Decomposers use the carbon dioxide in the bodies of dead organisms for food or fuel. Decay and the Carbon Cycle. Over the long-term the decomposition of dead matter generates these fossil fuel products.
It is also put into the atmosphere by burning. Decomposition is the process by which bacteria and fungi break dead organisms into their simple compounds. Decomposition is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide water simple sugars and mineral salts.